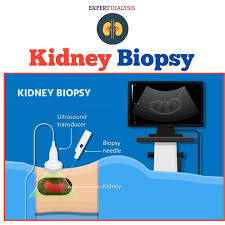
Kidney Biopsy
🧪 Kidney Biopsy (Renal Biopsy):
A kidney biopsy is a medical procedure in which a small piece of kidney tissue is removed for laboratory examination. It helps doctors diagnose the cause of kidney problems and determine the severity of kidney disease.
🩺 Why is it done?
A kidney biopsy is performed to:
Identify the cause of blood or protein in the urine
Diagnose kidney inflammation or autoimmune diseases (like lupus nephritis)
Evaluate the extent of kidney damage
Monitor a transplanted kidney
Guide treatment decisions for kidney disease
🔍 How is it performed?
The most common method is a percutaneous biopsy:
The procedure is usually done under local anesthesia.
A thin needle is inserted through the skin into the kidney, often using ultrasound or CT scan guidance.
A small tissue sample is collected.
In some cases, an open surgical biopsy may be needed.
⏱️ Duration & Recovery:
The procedure usually takes 30 to 60 minutes.
Patients are monitored for a few hours afterward for bleeding or complications.
Rest is advised for 24–48 hours post-biopsy.